Even though transistors were an efficient way to amplify current another device to achieve the same came into existence.The field effect transistors were similar in operation the transistor .The basic difference between the BJT and FET is that BJT is a current controlled device whereas FET is a voltage controlled device.
The images of the bjt and fet are mentioned below:
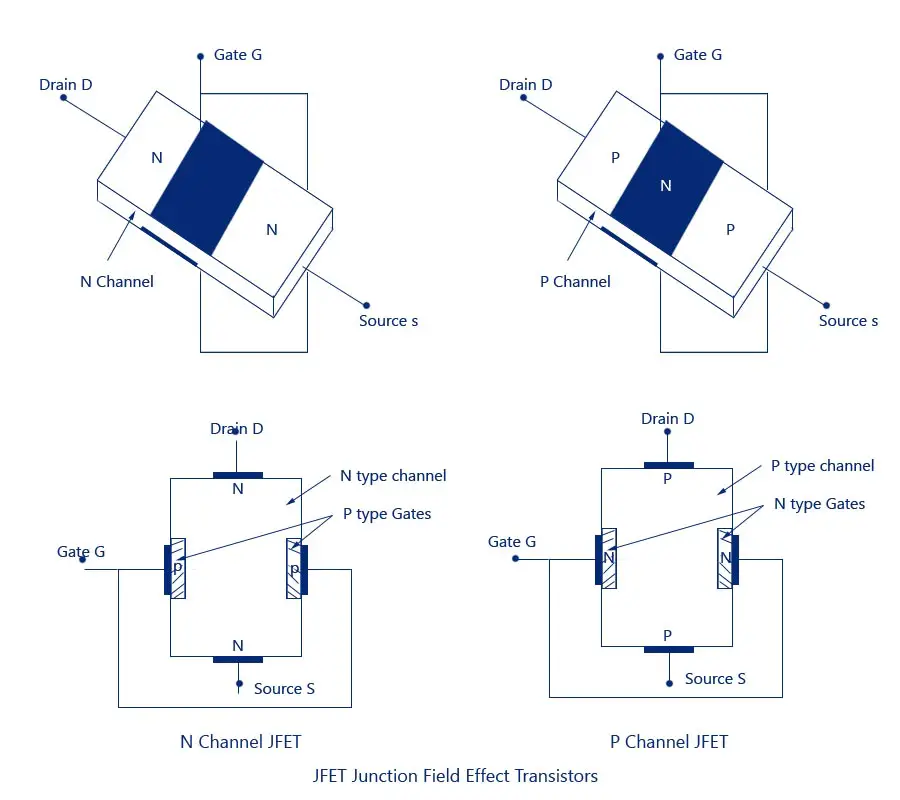
There are two types of FET.They are
a.the junction field effect transistor
b.the Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor
Further the JFET has two types i.e
a. the n channel and
b.p channel FET.
Also the MOSFET has two types i.e
a.the enhancement and
b.depletion type MOSFET.
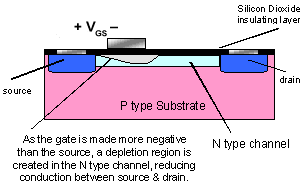
As can be seen from the diagram above the FET consists of three components i.e the source ,the drain and the gate.
The working of a FET can be compared to the water flowing down a tap.By controlling the tap screw the flow of water through the tap can be controlled .Similarly the gate is analogous to the tap screw,by controlling the gate voltage the flow of electrons from the source to the drain can be controlled.
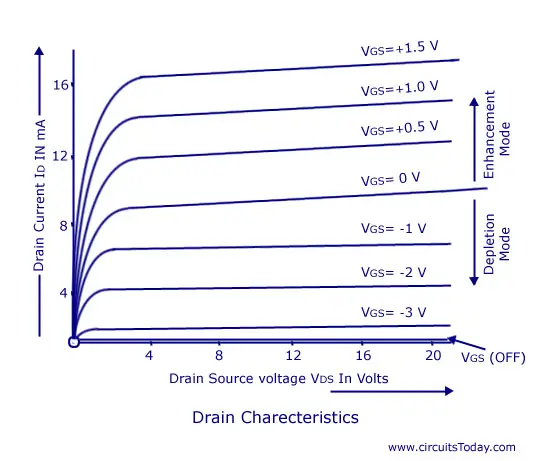
Characteristics of a n channel JFET:
When Vgs=0 and Vds is increased:
Since the gate voltage is zero the depletion layers are unaffected.
so the drain current increases with an increase in Drain to source voltage.
When Vgs<0 and Vds is increased:
As Vgs is very low the increase in Vds further increases the depletion layer and reaches a point called pinch-off where the drain current settles .Beyond the pinch off voltage the drain current is constant
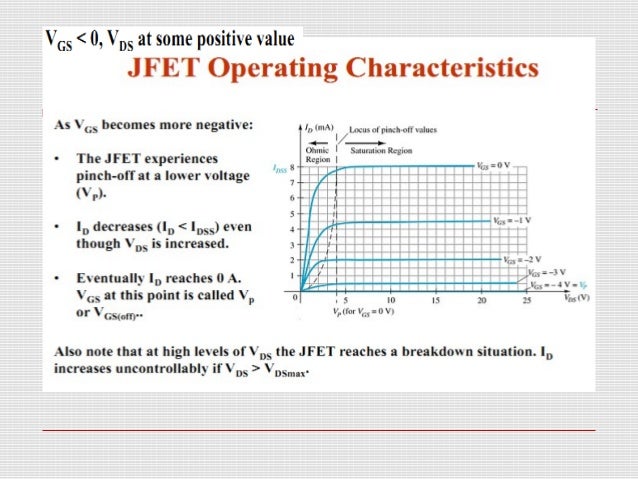
The pinch off voltage is negative for a n channel jfet and positive for a p-channel jfet.
Types of Mosfet:
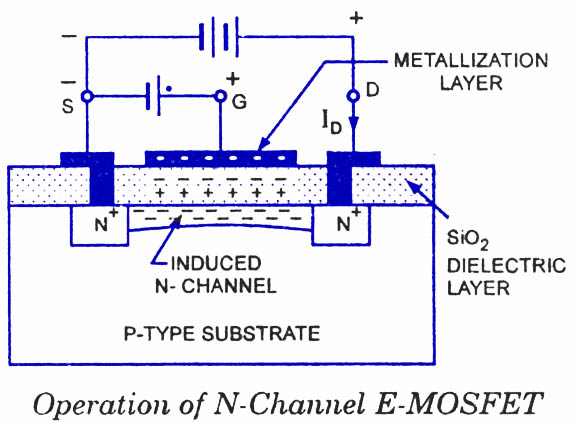
a.the enhancement type of MOSFET
Enhancement-mode MOSFETs are the common switching elements in most MOS. These devices are off at zero gate–source voltage, and can be turned on by pulling the gate voltage either higher than the source voltage, for NMOS, or lower than the source voltage, for PMOS. In most circuits, this means pulling an enhancement-mode MOSFET's gate voltage towards its drain voltage turns it ON.
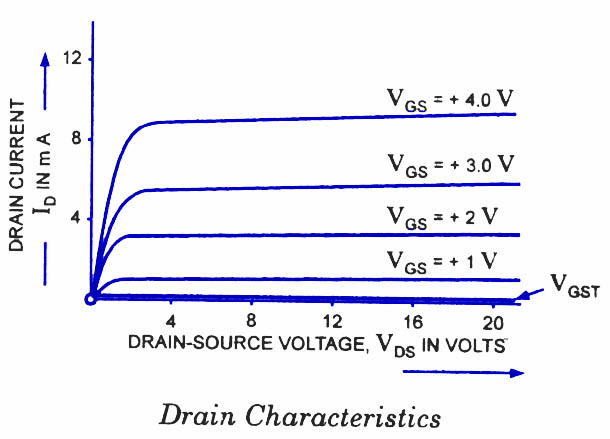
The enhancement mosfet has drain characteristics similar to the
JFET.
b.depletion type MOSFET
In a depletion-mode MOSFET, the device is normally ON at zero gate–source voltage. Such devices are used as load "resistors" in logic circuits (in depletion-load NMOS logic, for example). For N-type depletion-load devices, the threshold voltage might be about –3 V, so it could be turned off by pulling the gate 3 V negative (the drain, by comparison, is more positive than the source in NMOS). In PMOS, the polarities are reversed.
In the N channel device, shown in Fig. 5.2 the gate is made negative with respect to the source, which has the effect of creating a depletion area, free from charge carriers, beneath the gate. This restricts the depth of the conducting channel, so increasing channel resistance and reducing current flow through the device.
What do you think to add more like fet basics
ReplyDeleteyou are clear my mind actually after reading your article i got clear my complete doubt. thanks for such easy understanding post. I also got some similar at here just for your info i post here link may be useful for future aspect difference between enhancement and depletion type mosfet
ReplyDelete